Constructivism, Assimilation, and Accommodation
Author: Rebekah Black, Genevieve Cook, and Rebecca Marshall
Disclosure: ChatGPT3 was used in the creation of this resource.
Constructivism is a theory of learning in education suggesting that learners construct their understanding of the world through active participation and personal experiences. This type of learning emphasizes hands-on activities, problem-solving, and collaboration as essential elements of the learning process. In constructivism, teachers play the role of facilitators, scaffolding and supporting students in their exploration and construction of knowledge. This approach promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a deeper understanding of subjects by fostering students' active participation and engagement in the learning process. There are three types of constructivism: cognitive constructivism, social constructivism, and radical constructivism.
Cognitive constructivism: Knowledge is constructed by learners through organizing, interpreting, and integrating new information on top of their existing mental frameworks or schemas. They make connections between new ideas and their prior knowledge, resulting in the development of more complex and sophisticated mental structures.
Social constructivism: Social constructivism suggests that learning is a social process that occurs through interactions with others and the shared construction of meaning.
Radical constructivism: Radical constructivism is where individuals construct their understanding of the world based on their experiences, perceptions, and mental frameworks.

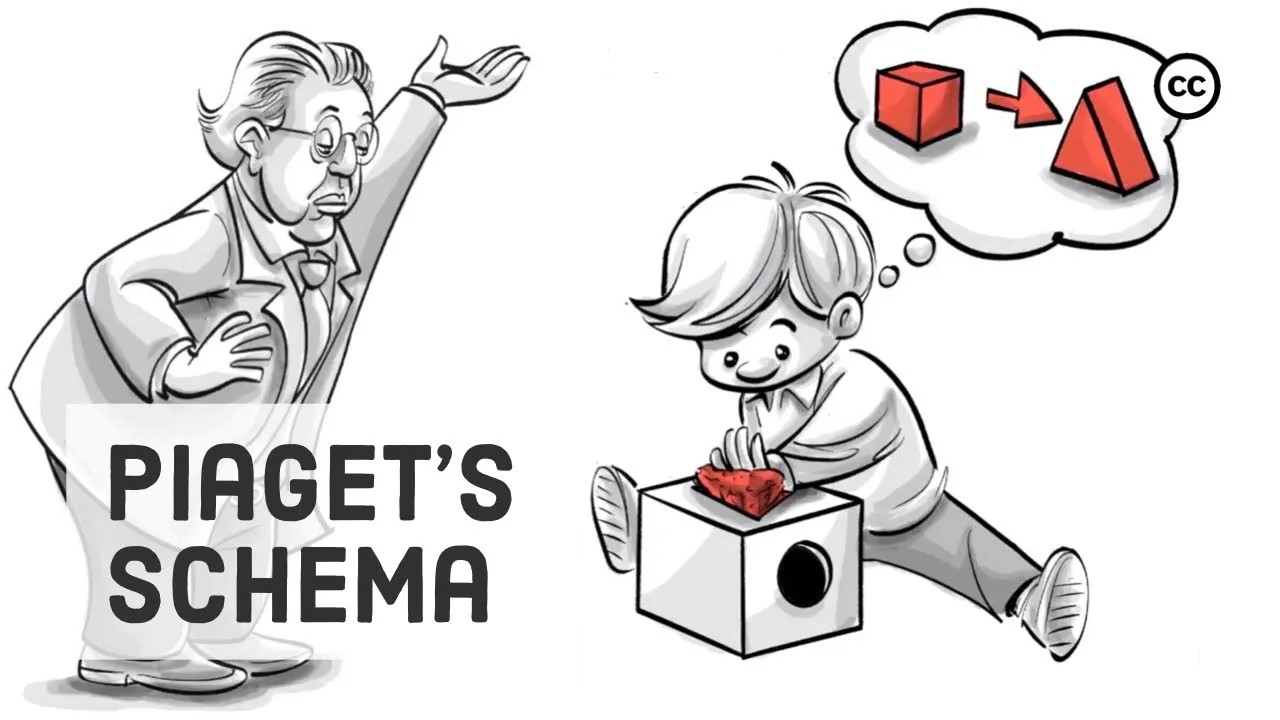
Jean Piaget proposed two terms called assimilation and accommodation as part of his cognitive developmental theory. Both assimilation and accommodation are processes of adapting new information into schemas. Assimilation is the process of making new information fit into one's existing understanding. When individuals encounter new information, they will often try to make sense of it by relating it to what they already know. This process can happen automatically and unconsciously, and it can help individuals make sense of the world around them. When encountering new information, individuals will often try to fit it into their existing schemas. This can help them understand the new information more quickly and easily, but it can also lead to misunderstandings or biases if the new information does not fit well with the existing schemas.
Accommodation is the process of changing or replacing one's existing understanding to incorporate new information. When individuals encounter new information or experiences that do not fit within their existing schemas, they need to adapt their thinking and create new cognitive structures to incorporate the new information.
Teacher Connections
- Understanding constructivism can help teachers create more effective and engaging learning environments by focusing on student-centered, active learning and encouraging critical thinking and reflection.
- Understanding the processes of assimilation and accommodation can help teachers better support students in adapting to new information and developing a deep understanding of the material.
In teaching, assimilation, accommodation, and constructivism are interrelated concepts that help students to learn and construct new knowledge. Assimilation involves integrating new information into existing mental models or schemas. Accommodation involves modifying existing mental structures to accommodate new information that does not fit into pre-existing schemas. Constructivism emphasizes the active role of the learner in constructing new knowledge and understanding through interaction with the environment. Effective teaching involves providing students with opportunities to assimilate new information into their existing schemas, facilitating accommodation when new information challenges existing mental models, and fostering constructivist learning by allowing students to actively construct their knowledge through exploration and discovery. By using these approaches, teachers can help students develop a deeper understanding of the material and construct their mental models and schemas.
Vocabulary/Terms to know
Constructivism: A theory of learning that suggests individuals construct their understanding and knowledge through experiences and interactions with the environment.
Schema: Mental structures or frameworks that organize knowledge and guide behavior.
Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD): The gap between what a learner can do on their own and what they can do with guidance or support.
Accommodation: The process of modifying existing schemas or creating new ones in response to new experiences or information.
Assimilation: The process of achieving balance or equilibrium between existing schemas and new information through accommodation and assimilation.
Quiz Questions
1. What is the difference between assimilation and accommodation?
- A. Assimilation is the process of making new information fit into one's existing understanding, while accommodation is the process of forgetting old information to make room for new information.
- B. Assimilation is the process of changing or replacing one's existing understanding to incorporate new information, while accommodation is the process of adding new information to existing schemas.
- C. Assimilation is the process of creating new schemas, while accommodation is the process of fitting new information into old schemas.
- D. Assimilation is the process of adding new information to existing schemas, while accommodation is the process of changing or replacing one's existing understanding to incorporate new information.
2. What is constructivism?
- A. A theory that people construct their knowledge and understanding based on their experiences and interactions with the world.
- B. A teaching method that emphasizes rote memorization and repetition of information.
- C. A method of learning that emphasizes the use of technology and multimedia resources.
- D. A psychological theory that states that individuals have innate abilities and skills that can be developed through training and practice.
3. What is the goal of a constructivist classroom?
- A. To encourage students to memorize facts and information as quickly as possible.
- B. To help students develop critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of the material.
- C. To create a competitive and individualistic learning environment.
- D. To teach students how to use technology and multimedia resources.
This content is provided to you freely by BYU-I Books.
Access it online or download it at https://books.byui.edu/development_motivati/mod_92_constructivis.



